Chemistry Acid and Bases (Conjugates) PO4 3- + HNO3—> NO3 – +HPO4 2- What is the conjugate acid in the following equation? Click the card to flip 👆 HPO4 2- Click the card to flip 👆 1 / 17 Flashcards Learn Test Match Q-Chat Created by aiaslam Students also viewed polyatomic ions 17 terms HauMPRM Preview Polyatomic Ions (group 1) 26 terms
Write equations for the following acid–base reactions. Label the … | Channels for Pearson+
BRIAN M. May 11, 2014. Let us take the example of Bicarbonate being placed in water to create Carbonic Acid and Hydronium ions. H CO− 3 +H 2O → H 2CO3 +OH −. Base + Acid → ConjA+ ConjB. On the reactant side of the equation the water ( H 2O) is the Acid as it is the hydrogen ion donor to the bicarbonate ( H CO− 3) which is the Base as

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
Exercise 8.22.1 8.22. 1. Identify the conjugate pairs in the following Brønsted-Lowry acid/base equation, and label each of the given chemical formulas as corresponding to a Brønsted-Lowry acid, a Brønsted-Lowry base, a conjugate acid, or a conjugate base. C2H5OH C 2 H 5 OH + H2O H 2 O ↽−−⇀ ↽ − − ⇀ C2H5OH+12 C 2 H 5 OH 2 + 1

Source Image: scribd.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Question 1A: Conjugate Acids Bases In the following reaction: HCIO H2SO4 CIO- H3SO4+ HCIO is the acid and H2SO4 is its conjugate base. HCIO is the acid and CIO- is its A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid gives a proton (H +) to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as it loses a hydrogen ion in the reverse reaction. On the other hand, a conjugate base is what remains after an acid has donated a proton during a chemical reaction.

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Which Is The Conjugate Acid In The Following Reaction
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid gives a proton (H +) to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as it loses a hydrogen ion in the reverse reaction. On the other hand, a conjugate base is what remains after an acid has donated a proton during a chemical reaction. Introductory Chemistry Online! (Young) 8: Acids, Bases and pH
Solved 2. Which is the conjugate acid in the following | Chegg.com
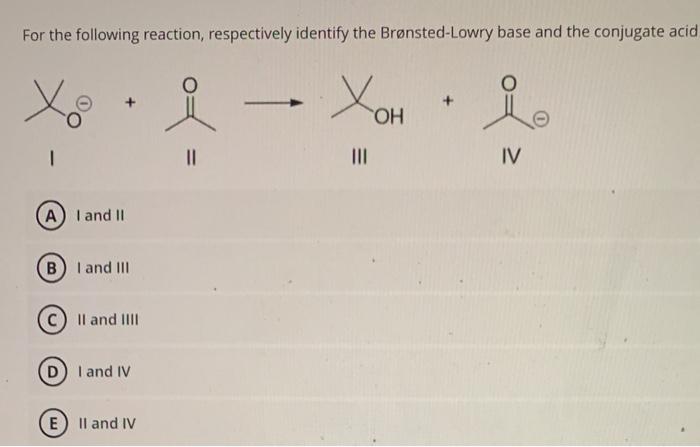
The conjugate acid of a Brønsted-Lowry base is the species formed after a base accepts a proton. The two species in a conjugate acid-base pair have the same molecular formula except the acid has an extra H + compared to the conjugate base. Introduction A fish market where a variety of fresh and packaged fish are displayed on ice. Solved For the following reaction, respectively identify the | Chegg.com
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases | Conjugate Acid Base Pairs The conjugate acid of a Brønsted-Lowry base is the species formed after a base accepts a proton. The two species in a conjugate acid-base pair have the same molecular formula except the acid has an extra H + compared to the conjugate base. Introduction A fish market where a variety of fresh and packaged fish are displayed on ice.

Source Image: chemistrynotes.com
Download Image
Write equations for the following acid–base reactions. Label the … | Channels for Pearson+ Chemistry Acid and Bases (Conjugates) PO4 3- + HNO3—> NO3 – +HPO4 2- What is the conjugate acid in the following equation? Click the card to flip 👆 HPO4 2- Click the card to flip 👆 1 / 17 Flashcards Learn Test Match Q-Chat Created by aiaslam Students also viewed polyatomic ions 17 terms HauMPRM Preview Polyatomic Ions (group 1) 26 terms

Source Image: pearson.com
Download Image
SOLVED: Question 1A: Conjugate Acids Bases In the following reaction: HCIO H2SO4 CIO- H3SO4+ HCIO is the acid and H2SO4 is its conjugate base. HCIO is the acid and CIO- is its Exercise 8.22.1 8.22. 1. Identify the conjugate pairs in the following Brønsted-Lowry acid/base equation, and label each of the given chemical formulas as corresponding to a Brønsted-Lowry acid, a Brønsted-Lowry base, a conjugate acid, or a conjugate base. C2H5OH C 2 H 5 OH + H2O H 2 O ↽−−⇀ ↽ − − ⇀ C2H5OH+12 C 2 H 5 OH 2 + 1

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Acid Base Reaction: Over 871 Royalty-Free Licensable Stock Illustrations & Drawings | Shutterstock Identify conjugate acid and conjugate base in the following reaction. H 2 PO 4 − (aq) + H 2 O (l) ⇌ HPO 4 2 − (aq) + H 3 O + (aq). a) HPO 4 2 − (conjugate acid), H 3 O + (conjugate base) . b) HPO 4 2 − (conjugate base), H 3 O + (conjugate acid). c) H 2 PO 4 − (conjugate acid), H 2 O (conjugate base). d) H 2 PO 4 − (conjugate base), H 2 O (conjugate acid)

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
2.349 lowry afbeeldingen, stockfoto’s, 3D-objecten en vectoren | Shutterstock A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid gives a proton (H +) to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as it loses a hydrogen ion in the reverse reaction. On the other hand, a conjugate base is what remains after an acid has donated a proton during a chemical reaction.

Source Image: shutterstock.com
Download Image
Chemistry Q and A Introductory Chemistry Online! (Young) 8: Acids, Bases and pH

Source Image: facebook.com
Download Image
Bronsted-Lowry Acids and Bases | Conjugate Acid Base Pairs
Chemistry Q and A BRIAN M. May 11, 2014. Let us take the example of Bicarbonate being placed in water to create Carbonic Acid and Hydronium ions. H CO− 3 +H 2O → H 2CO3 +OH −. Base + Acid → ConjA+ ConjB. On the reactant side of the equation the water ( H 2O) is the Acid as it is the hydrogen ion donor to the bicarbonate ( H CO− 3) which is the Base as
SOLVED: Question 1A: Conjugate Acids Bases In the following reaction: HCIO H2SO4 CIO- H3SO4+ HCIO is the acid and H2SO4 is its conjugate base. HCIO is the acid and CIO- is its 2.349 lowry afbeeldingen, stockfoto’s, 3D-objecten en vectoren | Shutterstock Identify conjugate acid and conjugate base in the following reaction. H 2 PO 4 − (aq) + H 2 O (l) ⇌ HPO 4 2 − (aq) + H 3 O + (aq). a) HPO 4 2 − (conjugate acid), H 3 O + (conjugate base) . b) HPO 4 2 − (conjugate base), H 3 O + (conjugate acid). c) H 2 PO 4 − (conjugate acid), H 2 O (conjugate base). d) H 2 PO 4 − (conjugate base), H 2 O (conjugate acid)